Kafka in the Enterprise for Admins

Monitoring and Operations
- Kafka exposes metrics through JMX
- Common places to host
- ELK
- Datadog
- New Relic etc
Important metrics:
- Under replication partitions (potentially high load on the cluster)
- Request handlers: use of threads for IO/network overall utizilation of an apache kafka broker
- Request timing: how long it takes to reply to request, lower is better as latency will be improved
Operations team must be able to:
- Rolling restart of brokers
- Update configuration
- Rebalance partitions
- Increase replication factor
- Add, replace, remove broker
- Upgrade cluster
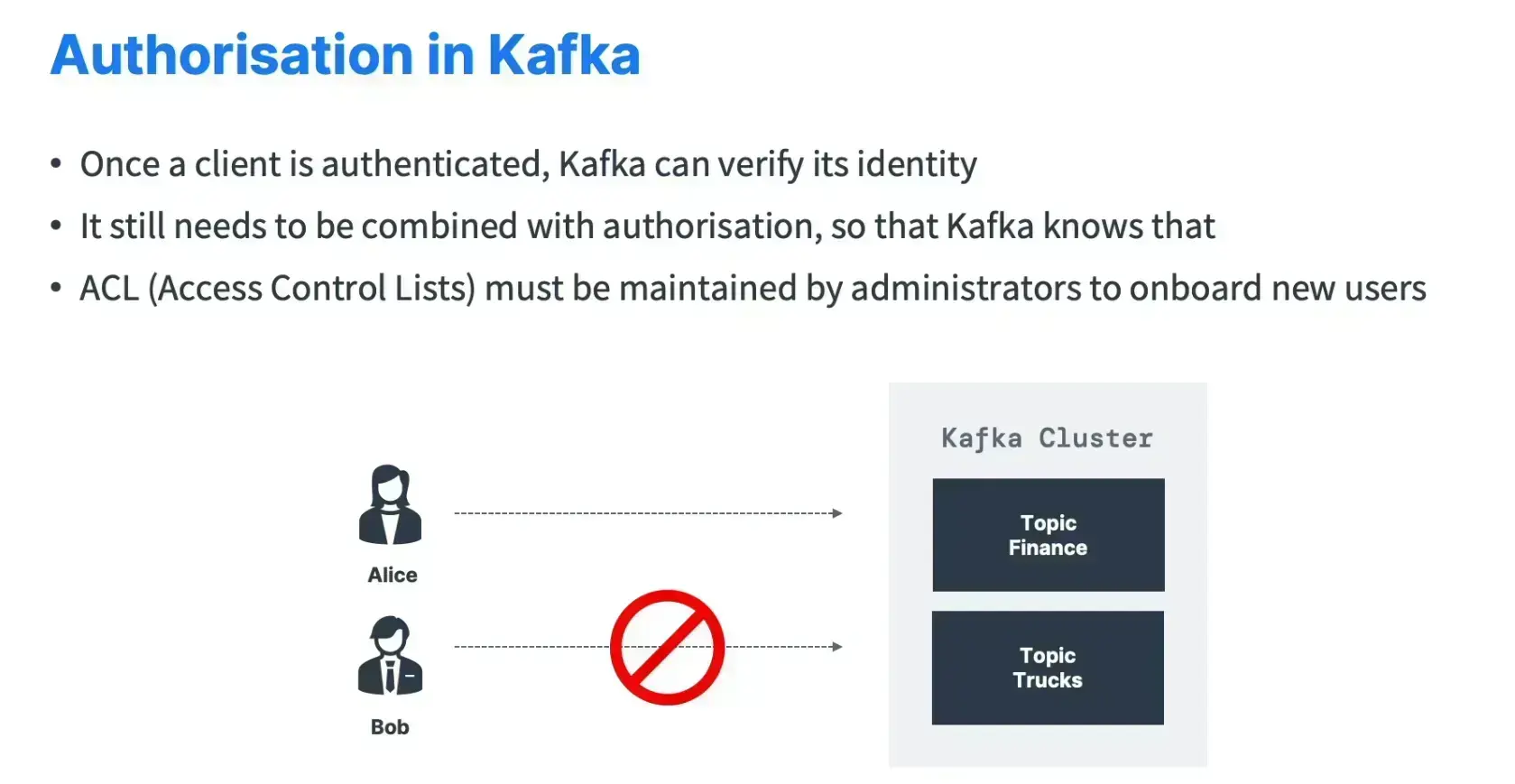
Kafka Security
Need to setup
- Authentication
- Authorization
- Encryption

References
Flashcards
If you enable an SSL endpoint in Kafka, what feature of Kafka will be lost?:: Zero copy. With SSL, messages will need to be encrypted and decrypted, by being first loaded into the JVM, so you lose the zero copy optimization.
What is not a valid authentication mechanism in Kafka?:: SAML
What is the protocol used by Kafka clients to securely connect to the Confluent REST Proxy?:: HTTPS (SSL/TLS) TLS - but it is still called SSL.
Kafka Multi Cluster and MirrorMaker
Kafka can only operate well in a single region, so we need to leverage replication
Mirror Maker 2 - Open source Kafka connector that ships with Kafka
Replicating doesn't preserve offsets, just data. Data at an offset in one cluster is not the same as the data at same offset in another cluster.
Replication: Active/Active, or Active/Passive (readonly)
References
Flashcards
Event-Driven Architecture Is an Integration Model Built Around the Publication, Capture, Processing, and Storage of Application or Service Events

Metadata
Highlights
Event messaging or publish/subscribe
In the event messaging or publish/subscribe model, event consumers subscribe to a class or classes of messages published by event producers. When an event producer publishes an event, the message is sent directly to all subscribers who want to consume it.
Typically a message broker handles the transmission of event messages between publishers and subscribers. The broker receives each event message, translates it if necessary, maintains its order relative to other messages, makes them available to subscribers for consumption, and then deletes them once they are consumed (so that they cannot be consumed again). (View Highlight) #✂️ ^ref-691986267
Event streaming
In the event streaming model, event producers publish streams of events to a broker. Event consumers subscribe to the streams, but instead of receiving and consuming every event as it is published, consumers can step into each stream at any point and consume only the events they want to consume. The key difference here is that the events are retained by the broker even after the consumers have received them. (View Highlight) #✂️ ^ref-691986302
A data streaming platform, such as Apache Kafka, manages the logging and transmission of tremendous volumes of events at very high throughput (literally trillions of event records per day, in real-time, without performance lag). A streaming platform offers certain characteristics a message broker does not:
• Event persistence: Because consumers may consume events at any time after they are published, event streaming records are persistent—they are maintained for a configurable amount of time, anywhere from fractions of a second to forever. This enables event stream applications to process historical data, as well as real-time data.
• Complex event processing: Like event messaging, event streaming can be used for simple event processing, in which each published event triggers transmission and processing by one or more specific consumers. But, it can also be used for complex event processing, in which event consumers process entire series of events and perform actions based on the result. (View Highlight) #✂️ ^ref-691986314
Not surprisingly, event-driven architecture is widely considered best practice for microservices implementations. Microservices can communicate with each other using REST APIs. But REST, a request/response integration model, undermines many of the benefits of the loosely coupled microservices architecture by forcing a synchronous, tightly coupled integration between the microservices. (View Highlight) #✂️ ^ref-691986441